How to make a good teacher
How to make a good teacher
What matters in schools is teachers. Fortunately, teaching can be taught
But efforts to ensure that every teacher can teach are hobbled by the tenacious myth that good teachers are born, not made. Classroom heroes like Robin Williams in “Dead Poets Society” or Michelle Pfeiffer in “Dangerous Minds” are endowed with exceptional, innate inspirational powers. Government policies, which often start from the same assumption, seek to raise teaching standards by attracting high-flying graduates to join the profession and prodding bad teachers to leave. Teachers’ unions, meanwhile, insist that if only their members were set free from central diktat, excellence would follow.
The premise that teaching ability is something you either have or don’t is mistaken. A new breed of teacher-trainers is founding a rigorous science of pedagogy. The aim is to make ordinary teachers great, just as sports coaches help athletes of all abilities to improve their personal best (see article). Done right, this will revolutionise schools and change lives.
Quis docebit ipsos doctores?
Education has a history of lurching from one miracle solution to the
next. The best of them even do some good. Teach for America, and the
dozens of organisations it has inspired in other countries, have brought
ambitious, energetic new graduates into the profession. And dismissing
teachers for bad performance has boosted results in Washington, DC, and
elsewhere. But each approach has its limits. Teaching is a mass
profession: it cannot grab all the top graduates, year after year. When
poor teachers are fired, new ones are needed—and they will have been
trained in the very same system that failed to make fine teachers out of
their predecessors.By contrast, the idea of improving the average teacher could revolutionise the entire profession. Around the world, few teachers are well enough prepared before being let loose on children. In poor countries many get little training of any kind. A recent report found 31 countries in which more than a quarter of primary-school teachers had not reached (minimal) national standards. In rich countries the problem is more subtle. Teachers qualify following a long, specialised course. This will often involve airy discussions of theory—on ecopedagogy, possibly, or conscientisation (don’t ask). Some of these courses, including masters degrees in education, have no effect on how well their graduates’ pupils end up being taught.
What teachers fail to learn in universities and teacher-training colleges they rarely pick up on the job. They become better teachers in their first few years as they get to grips with real pupils in real classrooms, but after that improvements tail off. This is largely because schools neglect their most important pupils: teachers themselves. Across the OECD club of mostly rich countries, two-fifths of teachers say they have never had a chance to learn by sitting in on another teacher’s lessons; nor have they been asked to give feedback on their peers.
Those who can, learn
If this is to change, teachers need to learn how to impart knowledge
and prepare young minds to receive and retain it. Good teachers set
clear goals, enforce high standards of behaviour and manage their lesson
time wisely. They use tried-and-tested instructional techniques to
ensure that all the brains are working all of the time, for example
asking questions in the classroom with “cold calling” rather than
relying on the same eager pupils to put up their hands.Instilling these techniques is easier said than done. With teaching as with other complex skills, the route to mastery is not abstruse theory but intense, guided practice grounded in subject-matter knowledge and pedagogical methods. Trainees should spend more time in the classroom. The places where pupils do best, for example Finland, Singapore and Shanghai, put novice teachers through a demanding apprenticeship. In America high-performing charter schools teach trainees in the classroom and bring them on with coaching and feedback.
Teacher-training institutions need to be more rigorous—rather as a century ago medical schools raised the calibre of doctors by introducing systematic curriculums and providing clinical experience. It is essential that teacher-training colleges start to collect and publish data on how their graduates perform in the classroom. Courses that produce teachers who go on to do little or nothing to improve their pupils’ learning should not receive subsidies or see their graduates become teachers. They would then have to improve to survive.
Big changes are needed in schools, too, to ensure that teachers improve throughout their careers. Instructors in the best ones hone their craft through observation and coaching. They accept critical feedback—which their unions should not resist, but welcome as only proper for people doing such an important job. The best head teachers hold novices’ hands by, say, giving them high-quality lesson plans and arranging for more experienced teachers to cover for them when they need time for further study and practice.
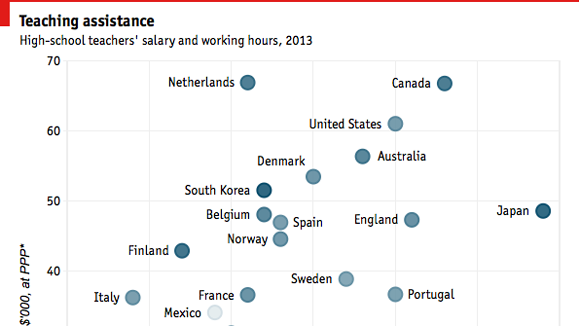
Money is less important than you might think. Teachers in top-of-the-class Finland, for example, earn about the OECD average. But ensuring that the best stay in the classroom will probably, in most places, mean paying more. People who thrive in front of pupils should not have to become managers to earn a pay rise. And more flexibility on salaries would make it easier to attract the best teachers to the worst schools.
Improving the quality of the average teacher would raise the profession’s prestige, setting up a virtuous cycle in which more talented graduates clamoured to join it. But the biggest gains will come from preparing new teachers better, and upgrading the ones already in classrooms. The lesson is clear; it now just needs to be taught.
Comments
Post a Comment